单例模式
介绍
程序运行周期内这个对象最多被创建一次,这类对象我们称之为单例,这个设计模式称作单例模式。
特点
1
2
3
4
5
6
| private Singleton() {
//do something
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
|
实现方式
饿汉式
代码示例
1
| private static Singleton instance = new Singleton();
|
优势
劣势
- 资源效率不高,当执行其它静态方法 或者 class.forName 时就会被初始化。
懒汉式
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public synchronized static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
|
优势
劣势
双重检查
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
|
优势
- 线程安全
- 第一次以后调用 不再受到 synchronize 影响;
劣势
- java内存模型(jmm)无序写入可能会引发,对象创建失败问题;
静态内部类
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
| private static class NoThing {
private static Singleton instance = new Singleton();
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return NoThing.instance;
}
|
优势
劣势
总结
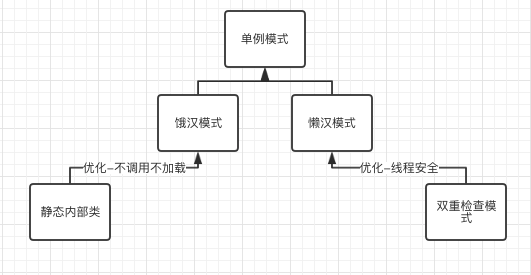
关系图谱
![upload successful]()
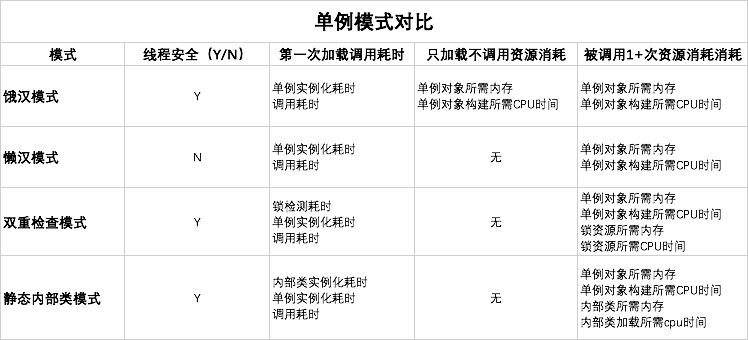
对比
![upload successful]()
个人观点
你会写一个 消耗资源且可能不被调用的单例吗?所以 就用饿汉模式吧。