概述
将对象组合成树形结构以表示”部分-整体“的层次结构,使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
类图
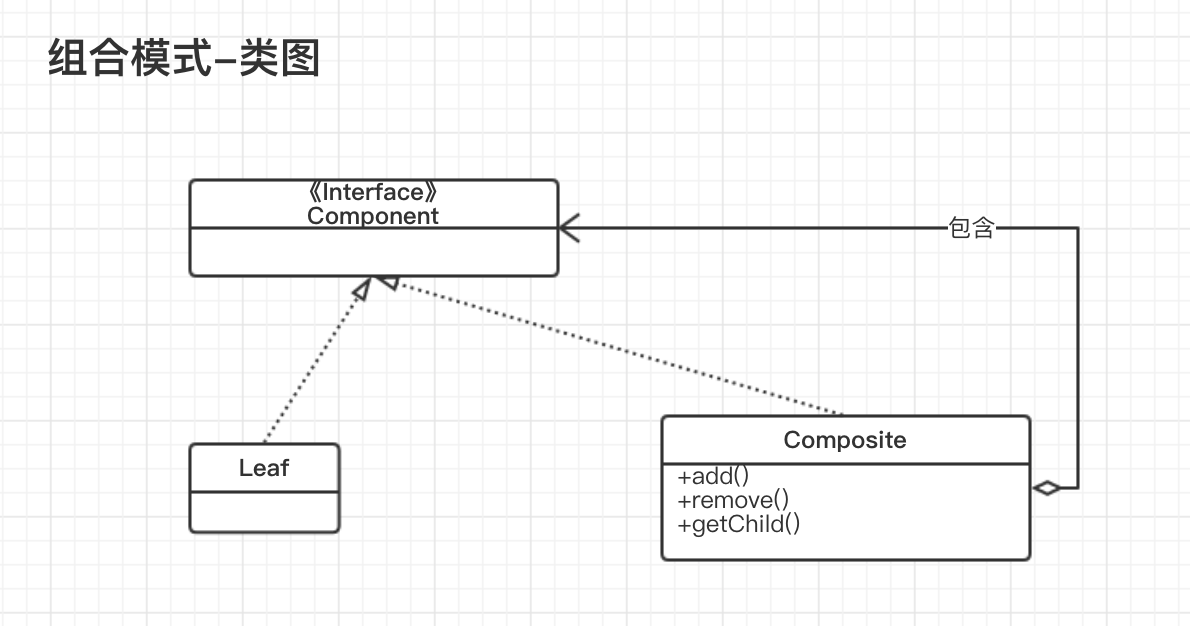
角色
- 抽象构件(Component)角色
该角色定义参加组合对象的共有方法和属性,规范一些默认的行为接口。 - 叶子构件(Leaf)角色
该角色是叶子对象,其下没有其他分支,定义出参加组合的原始对象行为。 - 树枝构件(Composite)角色
该角色代表参加组合的、其下有分支的树枝对象,他的作用是将树枝和叶子组合成一个树形结构,并定义出管理子对象的方法,如add()、remove()等。
示例
Component.java
1 | public interface Component{ |
Composite.java
1 | public class Composite implements Component{ |
Leaf.java
1 | public class Leaf implements Component{ |
Client.java
1 | public class Client{ |
应用
优点
- 高层模块调用简单。
一颗树形机构中的所有节点都是Component,局部和整体对调用者来说没有任何区别,即高层模块不必关心自己处理的是单个对象还是整个组合结构,简化了高层模块的代码。 - 节点自由增加。
使用组合模式后,如果想增加一个树枝节点、树叶节点只需要找到其父节点即可。
缺点
- 不易控制树枝结构的类型;
- 不易使用继承的方法来增加新的行为。
场景
- 需要描述对象的部分和整体的等级结构,如树形菜单、文件和文件夹管理。
- 需要客户端忽略个体构件和组合构件的区别,平等对待所有的构件。
组合模式也是应用广泛的一种设计模式,例如,java基础类库的swing部分中就大量使用了组合模式,大部分控件都是JComponent的子类,同时其add()方法又可向界面添加JComponent类型的控件,从而使得使用者可以统一的方式操作各种控件。
实例
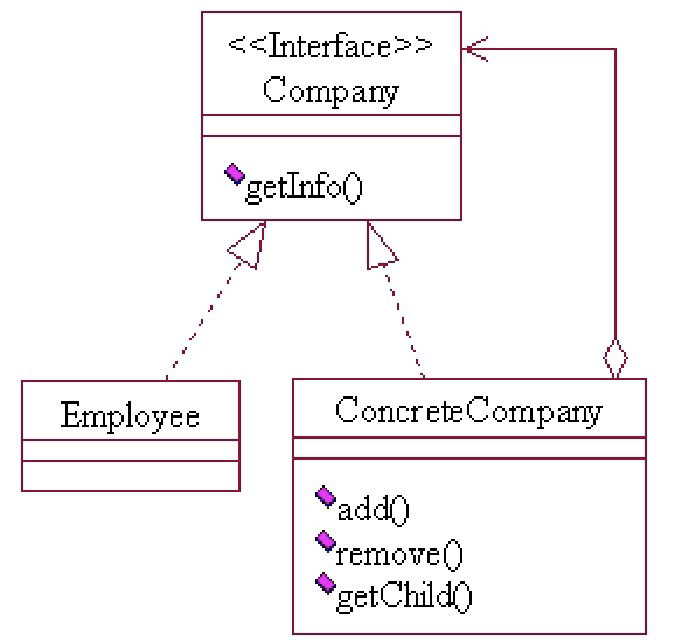
Company.java
1 | public interface Company{ |
ConcreteCompany.java
1 | //树枝节点类 |
Employee.java
1 | public class Employee implements Company{ |
ClientDemo.java
1 | public class ClientDemo{ |

